实验要求
cminus-f的词法分析和语法分析部分已经完成,最终得到的是语法分析树。而为了产生目标代码,还需要将语法分析树转为抽象语法树,通过抽象语法分析树生成中间代码(即IR),最后使用中间代码来进行优化并生成目标代码。在本实验中,只要完成中间表示IR的生成,语法分析树到抽象语法树的转换已经在框架中提供了,而IR代码到目标代码的生成由clang来完成。
生成IR指令的过程为在访问者模式下访问抽象语法树。本次实验要完成的就是访问抽象语法树的相关visit函数,在这些visit函数中要完成IR指令的生成。
实验难点
1.使用AST和visit函数生成IR指令
由于cminus-f的语法还是比lab3中计算器要复杂的多,供参考的抽象语法树的打印代码也还是和生成IR指令由很大差别,在开始编写时存在困难。通过阅读AST的头文件和lab3的visitor.cpp,首先确定了visit函数生成IR指令的过程:
- visit函数调用当前节点的子节点accept函数,即调用子节点的visit函数
- 处理当前节点,生成指令
若子节点需要向父节点传值,则通过全局变量来实现。在visit节点时还要加入语义分析的部分,判断语义是否正确。
为了进一步弄清楚遍历AST生成IR的过程,在各个visit函数中加入logging信息,也为后续排查错误做好准备。然后首先完成较为简单的表达式处理等部分,通过这个过程逐渐熟悉IR转换和层次关系以及传值的过程,最后完成困难的visit函数。并在实现过程中逐步用简单的cminus程序测试,用logging找到出错的位置,完成逐个函数的设计。
以第一个产生式program->declaration-list为例,首先找到节点的定义,program节点包含一个保存了declaration的vector,因此在visit中要逐个调用这些declaration节点的accept函数。Program只需要产生声明,不需要产生IR,只需要进行语义分析,在语义说明中给出了以下规则:
- 一个程序由一系列声明组成,声明包括了函数声明与变量声明,它们可以以任意顺序排列。
- 一个程序中至少要有一个声明且最后一个声明必须是 void main(void)形式的函数声明。
只需要对第二条进行检查,判断至少有一个声明,且最后一个声明是否是void main(void)形式的函数声明。在Declaration类型的节点中有id和type,进行检查即可,其中type是CminusType类型,在hpp开头枚举。因此Program节点的visit函数如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTProgram &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Program\n";
if(node.declarations.size()==0){
cout << "ERROR: 该程序中没有声明。\n";
return;
}
if(!(node.declarations.back()->id=="main"&& node.declarations.back()->type==TYPE_VOID)){
cout << "ERROR: 最后一个声明不是void main(void)";
return;
}
for(auto dec: node.declarations)
dec->accept(*this);
return;
}
|
2.函数参数的处理
在编写FunDeclaration和Param的visit函数时,不明确参数具体的处理方法。找到lab3中由clang生成的.ll,对于参数的处理都是先分配空间,然后使用store指令将参数值存入分配好的空间。例如以下程序:
1
2
3
4
5
| define i32 @callee(i32 %0) #0 {
%2 = alloca i32
store i32 %0, i32* %2
...
}
|
但是Param的参数只有id,表示的是源程序中的参数名,对于如何找到这个参数产生了疑惑。重新找到lab3中编写的cpp传参的部分,传参是在函数创建以后,通过Function中的iterator获取得到的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
std::vector<Value *> args;
for (auto arg = callee->arg_begin(); arg != callee->arg_end(); arg++) {
args.push_back(*arg);
}
auto mul = builder->create_imul(args[0], CONST_INT(110));
|
此处获取参数的部分,是直接按lab3提供的gcd_array.cpp仿照编写的,因为理解不够深入,所以在本实验处理参数时又产生了疑惑。回顾lab3此部分代码后,FunDeclaration中的参数存储的部分就没有问题了。与lab3不同的是,FunDeclaration是逐个调用Param的accept函数,完成存储空间分配的,所以需要一个全局变量在FunDeclaration和Param的visit函数之间传递arg。
3.ASTVar的处理
根据cminus的语义说明,Var可以是整型变量,浮点变量或数组变量。如果是数组变量,需要判断下标是否为负,如果为负则添加neg_idx_except指令退出程序,否则计算对应元素的地址(gep指令)。如果是数组,则下标可能是个表达式,需要确保表达式的返回结果为整型,然后才能进行取元素的操作。
从上面的语义说明可以理解Var是一种变量。但是下面的赋值语义说明:先找到var代表的变量地址(如果是数组,需要先对下标表达式求值),然后对右侧的表达式进行求值,求值结果将在转换成变量类型后存储在先前找到的地址中。同时,存储在var中的值将作为赋值表达式的求值结果。一开始结合Var节点中含有一个表达式,把这句话错误的理解为了在Var的visit函数内要完成找到地址,求表达式的值并赋值的指令。后来为了进一步理解Var变量的visit函数内要产生什么指令,继续阅读了剩下的产生式,最终找到Var出现的两种情况:
- expression→var = expression | simple-expression
- factor→(expression) | var | call | integer | float
这两种情况下对于var的处理是不同的。对于第一种情况,var是赋值表达式的一个组成部分,在访问赋值表达式时,应该访问Var,在全局变量ret中保存Var的地址,然后进行赋值,产生store指令;而第二种情况,应该将Var的值取出保存到ret中,作为因子参与计算表达式的计算。因此访问Var节点时,需要知道是从哪种情况访问的,为此添加一个全局变量ifAssign,如果访问赋值语句,就将该变量置为true,访问Var时返回地址。
解决了以上问题后,就可以根据是否有指向expression的指针判断是否为数组,然后取出相应的值或者地址了。如果是数组,还要对下标进行处理。如果下标为负则终止程序,这可以通过跳转到一个仅含终止指令的exitBasicBlock实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| auto ifNegative = builder->create_icmp_lt(idx, CONST_INT(0));
auto exitBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), node.id + "exit", func);
auto nextBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), node.id + "next", func);
builder->create_cond_br(ifNegative, exitBB, nextBB);
|
处理非数组变量比较简单,处理数组变量时又产生了问题,因为数组获取元素地址有两种方式,即lab3中的两种getelementptr,分别需要两个偏移和一个偏移。为了明确如何处理数组,得到数组元素的指针,重新比较两种数组的分配的IR形式:
- %1 = alloca [10 x i32]
- %1 = alloca i32*
可以看出,第一种分配的是数组,得到的是指向数组的指针。第二种分配的是指针,这个指针是数组的首地址,返回的值是一个指向指针的指针。因此取元素地址时,使用第一种分配方式,直接对%1使用两个偏移的getelementptr,就得到了元素的地址;使用第二种分配方式,需要先使用load取出指针(数组首地址),然后使用一个偏移获取元素地址。因此在Var的visit函数中,处理如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| auto var = scope.find(node.id);
if(var->get_type()->get_pointer_element_type()->is_array_type())
builder->create_gep(var, { CONST_INT(0), idx });
else if(var->get_type()->get_pointer_element_type()->is_pointer_type()){
var = builder->create_load(var);
var = builder->create_gep(var, { idx });
}
else
std::cout << "ERROR: 变量" << node.id << "不是一个数组\n";
|
处理好以上两个问题后,剩下的部分就比较简单了。最终完整的Var的visit函数如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTVar &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Var\n";
auto var = scope.find(node.id);
if(var==nullptr)
std::cout << "ERROR: 未声明的变量" << node.id << "\n";
if(node.expression==nullptr){
if(ifAssign){
ret = var;
ifAssign = false;
}
else{
if(var->get_type()->get_pointer_element_type()->is_array_type())
ret = builder->create_gep(var, {CONST_INT(0), CONST_INT(0)});
else
ret = builder->create_load(var);
}
return;
}
node.expression->accept(*this);
Value *idx = ret;
if(idx->get_type()->is_float_type())
idx = builder->create_fptosi(idx, INT32_Type);
auto func = builder->get_insert_block()->get_parent();
auto ifNegative = builder->create_icmp_lt(idx, CONST_INT(0));
auto exitBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), node.id + " exit", func);
auto nextBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), node.id + " next", func);
builder->create_cond_br(ifNegative, exitBB, nextBB);
builder->set_insert_point(exitBB);
auto fail = scope.find("neg_idx_except");
builder->create_call(static_cast<Function*>(fail), {});
builder->create_br(nextBB);
builder->set_insert_point(nextBB);
if(var->get_type()->get_pointer_element_type()->is_array_type())
builder->create_gep(var, { CONST_INT(0), idx });
else if(var->get_type()->get_pointer_element_type()->is_pointer_type()){
var = builder->create_load(var);
var = builder->create_gep(var, { idx });
}
else
std::cout << "ERROR: 变量" << node.id << "不是一个数组\n";
if(ifAssign){
ret = var;
ifAssign = false;
}
else
ret = builder->create_load(var);
}
|
4.表达式顺序错误
在完成了整个实验后,进行测试,发现无法通过最后一个testcase。打开12.minus查看代码,其中有函数调用和一些基本运算,一开始不确定错误在什么位置,因为此时编译已经没有问题了,只可能是语义处理的问题。经过一些尝试后,改写了lab4_test.py,将运行的结果与正确的结果输出,分别为-39和39,通过这个结果将错误定位到函数调用,然后检查生成的.ll代码,发现函数gcd中有一个减法,操作数的顺序错误。因此找到了加法表达式中创建指令时,传值传反了的错误。additive-expression的产生式为:additive-expression -→ additive-expression addop term | term。生成运算指令时,加法表达式的结果应该在左边,编写时没有注意到这个问题,所以导致了结果的错误。修改后,testcases全部通过。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| ......
if(node.op==OP_PLUS){
if(ifInt)
ret = builder->create_iadd(addRes, mulRes);
else
ret = builder->create_fadd(addRes, mulRes);
}
......
|
实验设计
1.全局变量与宏定义
补充了一个CONST_INT()宏定义获取常量值。INT32_Type和FLOAT_TYPE获取int32和float类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| #define CONST_INT(num) \
ConstantInt::get((int)num, module.get())
#define INT32_Type \
Type::get_int32_type(module.get())
#define FLOAT_Type \
Type::get_float_type(module.get())
|
全局变量ret用于节点返回值。arg用于传递参数。ifAssign表示访问Var节点时,应该返回值还是变量地址。
1
2
3
| Value* ret;
Value* arg;
bool ifAssign = false;
|
2.visit函数
Program
检查语义后,逐个访问declarations。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTProgram &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Program\n";
if(node.declarations.size()==0){
cout << "ERROR: 该程序中没有声明。\n";
return;
}
if(!(node.declarations.back()->id=="main"&& node.declarations.back()->type==TYPE_VOID)){
cout << "ERROR: 最后一个声明不是void main(void)";
return;
}
for(auto dec: node.declarations)
dec->accept(*this);
return;
}
|
Num
数值节点没有子节点,直接进行处理,根据type确认数值类型,然后将值保存到全局变量value中。根据语义规则,只能有整型和浮点数两个类型。但此处的检查是没有必要的,因为其他数据类型会在词法分析时被识别为标识符,在语法分析时就会产生错误。而VOID类型在变量声明时进行检查,保证变量声明只有整型和浮点型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTNum &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Num\n";
if(node.type == TYPE_INT)
ret = CONST_INT(node.i_val);
else if(node.type == TYPE_FLOAT)
ret = CONST_FP(node.f_val);
return;
}
|
VarDeclaration
根据节点的定义,节点中包含一个类型和一个指针,还有继承自ASTDeclaration的id。对于变量声明节点的处理,需要产生分配空间的IR,在处理时还要区分数组与一般变量(根据节点的指针是否为空区分),局部变量与全局变量。并且要把声明的变量放入当前作用域中,保证后续使用可以找到。根据语义规则,全局变量需要初始化为0,数组变量声明时,大小应该大于0。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTVarDeclaration &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "VarDeclaration\n";
Type *varType;
if(node.type==TYPE_INT)
varType = INT32_Type;
else if(node.type==TYPE_FLOAT)
varType = FLOAT_Type;
else
std::cout <<"ERROR: 在变量声明中,只有整型和浮点型可以使用\n";
if(scope.in_global()){
if(node.num==nullptr){
auto initializer = CONST_ZERO(varType);
auto globalVar = GlobalVariable::create(node.id, module.get(), varType, false, initializer);
scope.push(node.id, globalVar);
}
else{
if(node.num->i_val>0){
auto *array = ArrayType::get(varType, node.num->i_val);
auto initializer = CONST_ZERO(array);
auto globalVar = GlobalVariable::create(node.id, module.get(), array, false, initializer);
scope.push(node.id, globalVar);
}
else
std::cout << "ERROR: 数组长度必须大于0\n";
}
}
else{
if(node.num==nullptr){
auto localVar = builder->create_alloca(varType);
scope.push(node.id, localVar);
}
else{
if(node.num->i_val>0){
auto *array = ArrayType::get(varType, node.num->i_val);
auto localVar = builder->create_alloca(array);
scope.push(node.id, localVar);
}
else
std::cout << "ERROR: 数组长度必须大于0\n";
}
}
}
|
FunDeclaration
FunDeclaration节点包含一个形参列表param和复合语句compound-stmt。需要创建的IR是创建函数和创建函数的第一个BasicBlock的指令,然后处理复合语句。在进入函数时要进入函数作用域,创建函数时要处理参数与返回值。对于每个参数,用全局变量取出实参,调用accept函数进行处理,在Param的visit函数中完成存储空间的分配,并加入到函数作用域当中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTFunDeclaration &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "FunDeclaration\n";
Type *retType;
std::vector<Type *> paramType;
FunctionType *funType;
if(node.id=="main" && node.params.size()>0)
cout << "ERROR: main函数必须为void main(void)形式\n";
if(node.type==TYPE_INT)
retType = INT32_Type;
else if(node.type==TYPE_FLOAT)
retType = FLOAT_Type;
else if(node.type==TYPE_VOID)
retType = Type::get_void_type(module.get());
for(auto param : node.params){
if(param->isarray){
if(param->type==TYPE_INT)
paramType.push_back(Type::get_int32_ptr_type(module.get()));
else if(param->type==TYPE_FLOAT)
paramType.push_back(Type::get_int32_ptr_type(module.get()));
}
else{
if (param->type==TYPE_INT)
paramType.push_back(INT32_Type);
else if(param->type==TYPE_FLOAT)
paramType.push_back(FLOAT_Type);
}
}
funType = FunctionType::get(retType, paramType);
auto func = Function::create(funType, node.id, module.get());
scope.push(node.id, func);
scope.enter();
auto entryBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), node.id + "entry", func);
builder->set_insert_point(entryBB);
std::vector<Value*> args;
for (auto arg = func->arg_begin();arg != func->arg_end();arg++) {
args.push_back(*arg);
}
for (int i = 0;i < node.params.size();i++) {
auto param = node.params[i];
arg = args[i];
param->accept(*this);
}
node.compound_stmt->accept(*this);
if (builder->get_insert_block()->get_terminator() == nullptr) {
if (func->get_return_type()->is_void_type())
builder->create_void_ret();
else if (func->get_return_type()->is_float_type())
builder->create_ret(CONST_FP(0.0));
else
builder->create_ret(CONST_INT(0));
}
scope.exit();
}
|
Param
在处理参数时,要为参数分配空间,使参数能够保留在函数的作用域内。在lab3中自行编写.ll文件时直接使用参数,不进行存储,直接使用就可以实现相同的逻辑。但在将cminus转换为IR时,cminus的语义规定了每次函数调用都会产生一组独立内存的参数,因此为参数分配空间,并存入作用域。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTParam &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Param\n";
Value* paramP;
if (node.isarray) {
if (node.type==TYPE_INT)
paramP = builder->create_alloca(Type::get_int32_ptr_type(module.get()));
else if (node.type==TYPE_FLOAT)
paramP = builder->create_alloca(Type::get_float_ptr_type(module.get()));
}
else {
if (node.type==TYPE_INT)
paramP = builder->create_alloca(INT32_Type);
else if (node.type==TYPE_FLOAT)
paramP = builder->create_alloca(FLOAT_Type);
}
builder->create_store(arg, paramP);
scope.push(node.id, paramP);
}
|
CompoundStmt
每个函数内部都有一个复合语句,根据ASTCompoundStmt的定义,复合语句由局部声明和一系列语句构成。只需要逐个调用相应的accept函数,不需要产生IR。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTCompoundStmt &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "CompoundStmt\n";
for(auto local_declaration: node.local_declarations)
local_declaration->accept(*this);
for(auto statement: node.statement_list)
statement->accept(*this);
}
|
ExpressionStmt
ExpressionStmt对应一条表达式或空,只要表达式存在,就处理该表达式。
1
2
3
4
5
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTExpressionStmt &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "ExpressionStmt\n";
if (node.expression != nullptr)
node.expression->accept(*this);
}
|
SelectionStmt
SelectionStmt包含一个条件表达式,一个if语句块,还有可能存在的else语句块。先处理表达式,产生条件跳转语句。如果指向else语句块的指针为空,就说明只有if语句。考虑只有if的情况,在执行到if时,应该通过br指令条件跳转到if语句块或if后的部分。如果还有else语句,则通过br指令条件跳转到if语句块或else语句块,然后从这两个语句块的结尾返回或者跳转到ifelse语句之后的部分。因此在SelectionStmt的visit函数中应该至少生成三个BasicBlock,并生成br指令。根据else指针是否为空判断是否需要生成条件判断为false的BasicBlock。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTSelectionStmt &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "SelectionStmt\n";
auto func = builder->get_insert_block()->get_parent();
node.expression->accept(*this);
auto retType = ret->get_type();
Value* ifExpression;
if(retType->is_integer_type())
ifExpression = builder->create_icmp_gt(ret, CONST_ZERO(INT32_Type));
else
ifExpression = builder->create_fcmp_gt(ret, CONST_ZERO(FLOAT_Type));
auto ifBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), "ifBasicBlock", func);
auto elseBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), "elseBasicBlock", func);
auto afterIfBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), "afterIfBasicBlock", func);
if(node.else_statement==nullptr)
builder->create_cond_br(ifExpression, ifBB, afterIfBB);
else
builder->create_cond_br(ifExpression, ifBB, elseBB);
builder->set_insert_point(ifBB);
node.if_statement->accept(*this);
if (builder->get_insert_block()->get_terminator() == nullptr)
builder->create_br(afterIfBB);
if(node.else_statement!=nullptr){
builder->set_insert_point(elseBB);
node.else_statement->accept(*this);
if (builder->get_insert_block()->get_terminator() == nullptr)
builder->create_br(afterIfBB);
}
else
elseBB->erase_from_parent();
builder->set_insert_point(afterIfBB);
}
|
IterationStmt
与if语句类似,while迭代语句也有一个条件表达式,进行条件跳转。可以创建一个用于判断的ifBasicBlock,一个循环的loopBasicBlock,一个while语句后的afterWhileBasicBlock,添加相应的指令。当条件表达式为True时,进行ifBB->loopBB->ifBB的循环跳转。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTIterationStmt &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "IterationStmt\n";
auto func = builder->get_insert_block()->get_parent();
auto ifBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), "ifBasicBlock", func);
auto loopBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), "loopBasicBlock", func);
auto afterWhileBB = BasicBlock::create(module.get(), "afterWhileBasicBlock", func);
builder->create_br(ifBB);
builder->set_insert_point(ifBB);
node.expression->accept(*this);
auto retType = ret->get_type();
Value* ifExpression;
if(retType->is_integer_type())
ifExpression = builder->create_icmp_gt(ret, CONST_ZERO(INT32_Type));
else
ifExpression = builder->create_fcmp_gt(ret, CONST_ZERO(FLOAT_Type));
builder->create_cond_br(ifExpression, loopBB, afterWhileBB);
builder->set_insert_point(loopBB);
node.statement->accept(*this);
if (builder->get_insert_block()->get_terminator() == nullptr)
builder->create_br(ifBB);
builder->set_insert_point(afterWhileBB);
}
|
ReturnStmt
返回语句中有一个表达式计算返回值,如果指向该返回语句的指针为空,说明没有返回值,创建一个void返回IR,否则需要调用该表达式的accept函数,并检查返回类型是否和函数的返回类型相同。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTReturnStmt &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "ReturnStmt\n";
if(node.expression==nullptr){
builder->create_void_ret();
return;
}
node.expression->accept(*this);
auto func = builder->get_insert_block()->get_parent();
auto retType = func->get_return_type();
auto resType = ret->get_type();
if (retType->is_integer_type() && resType->is_float_type())
ret = builder->create_fptosi(ret, INT32_Type);
else if(retType->is_float_type() && resType->is_integer_type())
ret = builder->create_sitofp(ret, FLOAT_Type);
builder->create_ret(ret);
}
|
Var
在实验难点中已说明。
AssignExpression
对于Assign语句,将全局变量ifAssign置为true,调用子节点var的accept函数得到变量的地址,然后计算表达式的值,创建store指令将值存入地址。需要确认表达式结果是否与变量类型相同,如果不同需要将表达式结果转换为和变量相同的类型。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTAssignExpression &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "AssignExpression\n";
ifAssign = true;
node.var->accept(*this);
auto varAdd = ret;
node.expression->accept(*this);
auto varType = varAdd->get_type()->get_pointer_element_type();
auto valueType = ret->get_type();
Value* value = ret;
if(varType!=valueType){
if(varType==INT32_Type)
value = builder->create_fptosi(ret, INT32_Type);
else
value = builder->create_sitofp(ret, FLOAT_Type);
}
builder->create_store(value, varAdd);
}
|
SimpleExpression
简单表达式SimpleExpression是一个加法表达式或两个加法表达式的关系运算。在节点中有两个加法表达式的指针和一个运算符类型为RelOp的运算符op,RelOp是一个枚举类型,包含了所有比较运算符。根据语义,对于该节点的处理,应该先处理加法表达式,将表达式的值保存下来,如果两个表达式指针都不为空,说明为关系运算,再比较两个运算结果,根据结果将表达式的值赋为0或1。进行比较时需要注意两个值的类型,整型和浮点型比较时要将整型转换为浮点型。
具体实现中,应该调用加法表达式的accept函数(如果指针不为空),暂存结果,对于比较运算,根据op生成icmp或fcmp的指令,最后返回的值就是指令结果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTSimpleExpression &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "SimpleExpression\n";
bool ifInt = true;
Value *resL, *resR;
Type *resLType, *resRType;
if(node.additive_expression_l!=nullptr){
node.additive_expression_l->accept(*this);
resL = ret;
resLType = ret->get_type();
}
if(node.additive_expression_r!=nullptr){
node.additive_expression_r->accept(*this);
resR = ret;
resRType = ret->get_type();
}
if(!(node.additive_expression_l!=nullptr && node.additive_expression_r!=nullptr)){
ret = (node.additive_expression_l!=nullptr) ? resL : resR;
return;
}
if(resLType!=resRType){
ifInt = false;
if(resLType->is_float_type())
resL = builder->create_sitofp(resL, FLOAT_Type);
else
resR = builder->create_sitofp(resR, FLOAT_Type);
}
switch (node.op)
{
case OP_LE:
if(ifInt)
ret = builder->create_icmp_le(resL, resR);
else
ret = builder->create_fcmp_le(resL, resR);
break;
default:
break;
}
ret = builder->create_zext(ret, INT32_Type);
}
|
AdditiveExpression
加法表达式中包含了一个乘法表达式,一个加法表达式和一个运算符。如果加法表达式指针为空,则表达式的值就是乘法表达式的值,否则分别计算两个表达式,调用相应的accept函数,然后进行根据运算符生成加或减指令。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTAdditiveExpression &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "AdditiveExpression\n";
bool ifInt = true;
if(node.additive_expression==nullptr){
node.term->accept(*this);
return;
}
node.additive_expression->accept(*this);
auto addRes = ret;
auto addType = addRes->get_type();
node.term->accept(*this);
auto mulRes = ret;
auto mulType = mulRes->get_type();
if(addType!=mulType){
ifInt = false;
if(addType->is_float_type())
mulRes = builder->create_sitofp(mulRes, FLOAT_Type);
else
addRes = builder->create_sitofp(addRes, INT32_Type);
}
if(node.op==OP_PLUS){
if(ifInt)
ret = builder->create_iadd(addRes, mulRes);
else
ret = builder->create_fadd(addRes, mulRes);
}
else{
if(ifInt)
ret = builder->create_isub(addRes, mulRes);
else
ret = builder->create_fsub(addRes, mulRes);
}
}
|
Term
乘法表达式由乘法表达式和因子或单独一个因子构成。与加法表达式的处理相同。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTTerm &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Term\n";
bool ifInt = true;
if(node.term==nullptr){
node.factor->accept(*this);
return;
}
node.term->accept(*this);
auto mulRes = ret;
auto mulType = mulRes->get_type();
node.factor->accept(*this);
auto factorRes = ret;
auto factorType = factorRes->get_type();
if(factorType!=mulType){
ifInt = false;
if(factorType->is_float_type())
mulRes = builder->create_sitofp(mulRes, FLOAT_Type);
else
factorRes = builder->create_sitofp(factorRes, INT32_Type);
}
if(node.op==OP_MUL){
if(ifInt)
ret = builder->create_imul(mulRes, factorRes);
else
ret = builder->create_fmul(mulRes, factorRes);
}
else{
if(ifInt)
ret = builder->create_isdiv(mulRes, factorRes);
else
ret = builder->create_fdiv(mulRes, factorRes);
}
}
|
Call
call节点需要创建一条函数调用call指令,从作用域中取出函数,然后根据函数的参数将节点的实参传入,并检查类型是否与函数参数的类型一致,不一致则需要转换为函数的形参类型。创建一个参数列表,将转换好的参数存入列表来调用函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| void CminusfBuilder::visit(ASTCall &node) {
LOG(DEBUG) << "Call\n";
auto func = static_cast<Function*>(scope.find(node.id));
auto paramType = func->get_function_type()->param_begin();
if(func==nullptr)
std::cout << "ERROR: 函数" << node.id << "未定义\n";
Value *temp;
std::vector<Value*> args;
for(auto arg: node.args){
arg->accept(*this);
temp = ret;
auto argType = ret->get_type();
if(argType!=*paramType)
if((*paramType)->is_integer_type())
temp = builder->create_fptosi(ret, INT32_Type);
else
temp = builder->create_sitofp(ret, FLOAT_Type);
args.push_back(temp);
paramType++;
}
builder->create_call(func, args);
}
|
实验总结
1.结果验证
在进行测试,改正编写过程中的一些错误后,编译后运行测试程序,所有测试样例都通过。
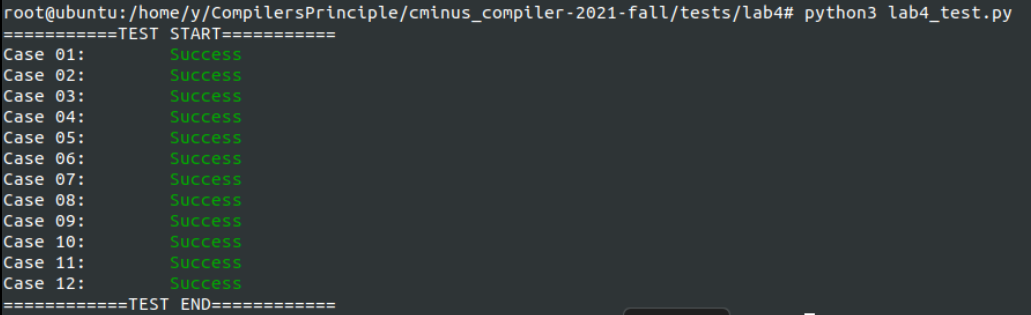
2.总结
通过本次实验,理解了从抽象语法树产生中间IR的方法,并进行了实现。在实现过程中,对于IR的指令有了进一步的熟悉与理解,掌握了使用C++接口创建不同IR指令的方法,以及在访问者模式下遍历抽象语法树,完成IR生成的过程。在完成实现时阅读了相关的头文件,语义规则,通过整个实验的框架复习了C++中一些概念和方法。经过四次实验,结合课程所学的原理,理解了编译器的词法分析,语法分析,中间代码生成的过程,也学习了相关工具的使用并进行了实践,清楚了编译器工作的每一个部分的原理和相互之间的配合。


